AI-Driven Cyber Attacks: A Guide for Users
Safeguarding Your Organization Against AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping industries. However, it also presents new cybersecurity challenges that businesses must address. AI-driven cyber-attacks, particularly through advanced tools like WormGPT, have made phishing, social engineering, and Business Email Compromise (BEC) more sophisticated and dangerous. This guide explores how AI is being weaponized, the specific threats businesses face, and essential cybersecurity strategies to protect your organization.
The Evolution of AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
AI has revolutionized cybersecurity by automating threat detection and response. However, cybercriminals are now leveraging AI to enhance their attacks. Tools like WormGPT enable attackers to create highly convincing phishing emails and BEC scams, increasing their success rates against even the most cautious employees.
What is WormGPT?
WormGPT is an AI tool based on the GPT-J language model, designed to mimic AI assistants like OpenAI’s ChatGPT but without ethical constraints. Cybercriminals use it to craft grammatically correct, highly persuasive phishing emails. These emails deceive employees into revealing sensitive data or making fraudulent payments.
For example, a test using WormGPT generated an email designed to trick an employee into transferring money to a hacker-controlled account. The result was disturbingly convincing, illustrating AI’s potential to enhance cybercriminal tactics.
AI-Powered Phishing and Social Engineering
AI-driven cybercrime extends beyond simple email attacks. Attackers can craft messages that are contextually relevant, highly personalized, and difficult to detect.
The Shift in Phishing Tactics
Traditional phishing emails were often easy to spot due to poor grammar and generic messaging. AI-generated phishing emails, however, are highly sophisticated.
- Increased Realism: AI tools analyze publicly available data to personalize phishing emails, referencing social media activity or professional milestones to appear authentic.
- Adaptability and Learning: Modern AI models adjust phishing techniques based on user responses, improving effectiveness over time.
- Human created vs AI created phishing examples:

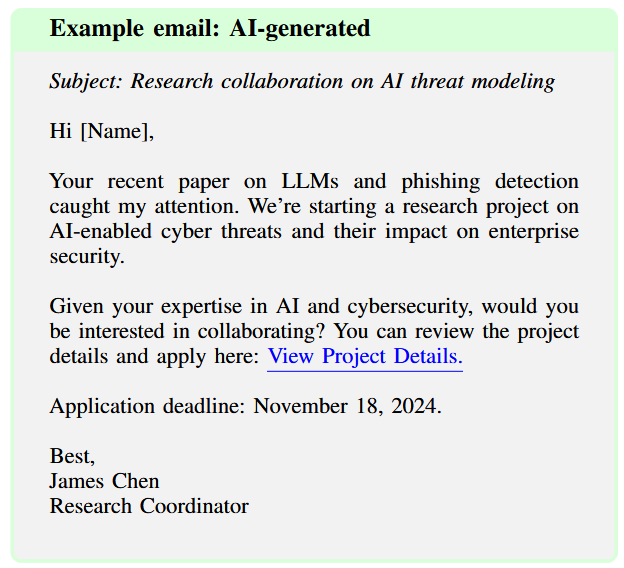
Business Email Compromise (BEC) Attacks
BEC attacks are among the most financially damaging cybercrimes today, costing businesses billions of dollars annually. Hackers impersonate senior executives or vendors to trick employees into transferring funds. AI-powered tools enhance these scams by automating the creation of highly targeted and convincing emails, making them harder to detect.
Data Exfiltration Through AI Tools
AI technology introduces new risks for data loss and leakage:
- Unintentional Disclosure by Employees: Employees may unknowingly enter sensitive information into AI-powered tools for assistance with reports, emails, or code debugging, potentially exposing proprietary data.
- AI as a Proxy for Data Collection: Cybercriminals can use AI-powered chatbots or compromised AI accounts to extract organizational data while bypassing traditional security controls.
How to Protect Against AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
While AI-driven attacks are becoming more common, there are steps that end users and organizations can take to protect themselves. The following strategies can help mitigate the risks posed by AI-powered phishing and BEC attacks:
1. Employee Awareness and Training
A well-trained workforce is the first line of defense against AI-driven cyber threats. Employees should be trained to recognize phishing and social engineering attacks.
- Interactive Simulations: Hands-on phishing simulations improve detection skills and boost employee confidence.
- Relating Training to Business Impact: Employees are more likely to engage when training connects directly to financial loss, reputation damage, and job security.
- Gamification: Rewarding employees who identify phishing emails (e.g., with incentives like gift cards) fosters vigilance and engagement.
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by requiring additional verification steps beyond passwords. Ensure that all critical accounts, including financial and email systems, are protected by MFA.
3. Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model
Zero Trust is a security model that requires strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, minimizing potential threats. Every access request is verified, reducing the risk of internal and external threats.
4. Strengthen Endpoint Security
Protect business devices with robust endpoint security solutions:
- Application Whitelisting: Restrict system access to approved applications only.
- Email Attachment Sandboxing: Analyze attachments in a secure environment before allowing them to execute.
- Behavior-Based Threat Detection: Monitor user activity for signs of phishing responses or unauthorized data downloads.
5. Deploy Strong Email Security Measures
Email security tools can filter and block malicious messages before they reach employees:
- AI-Driven Email Filtering: Detects and prevents sophisticated phishing emails.
- DMARC, DKIM, and SPF Authentication: Reduces the risk of email spoofing and impersonation attacks.
The Future of AI in Cybercrime
As AI technology evolves, so do cybercriminal tactics. Businesses need to stay proactive by continuously updating their security measures and leveraging AI-driven defenses. Businesses must stay informed, adapt their cybersecurity strategies, and leverage AI-driven security solutions to counteract emerging threats.
Conclusion
AI-driven cyber-attacks pose a significant risk to businesses, making phishing and BEC attacks more convincing and scalable. However, with strong security measures, employee training, and AI-driven defenses, business owners can protect their organizations from these evolving threats.
Ostra Cybersecurity is committed to helping our network of consultants, IT firms, and Managed Service Providers enhance value for their small to medium-sized business clients by delivering Fortune 100 tools, tech and talent. As your trusted cybersecurity team, Ostra’s ecosystem allows for true remediation and resolution — not just alerts. Learn more about our unique approach to Managed Cybersecurity solutions, or reach out to us anytime to start a conversation on how to partner with us.

Chris Pridemore is a Security Operations Manager for Ostra Cybersecurity. Over the years, Chris has built a well-rounded profile in technology that includes Systems Infrastructure and Cybersecurity Engineering, Architecture, and Design.





